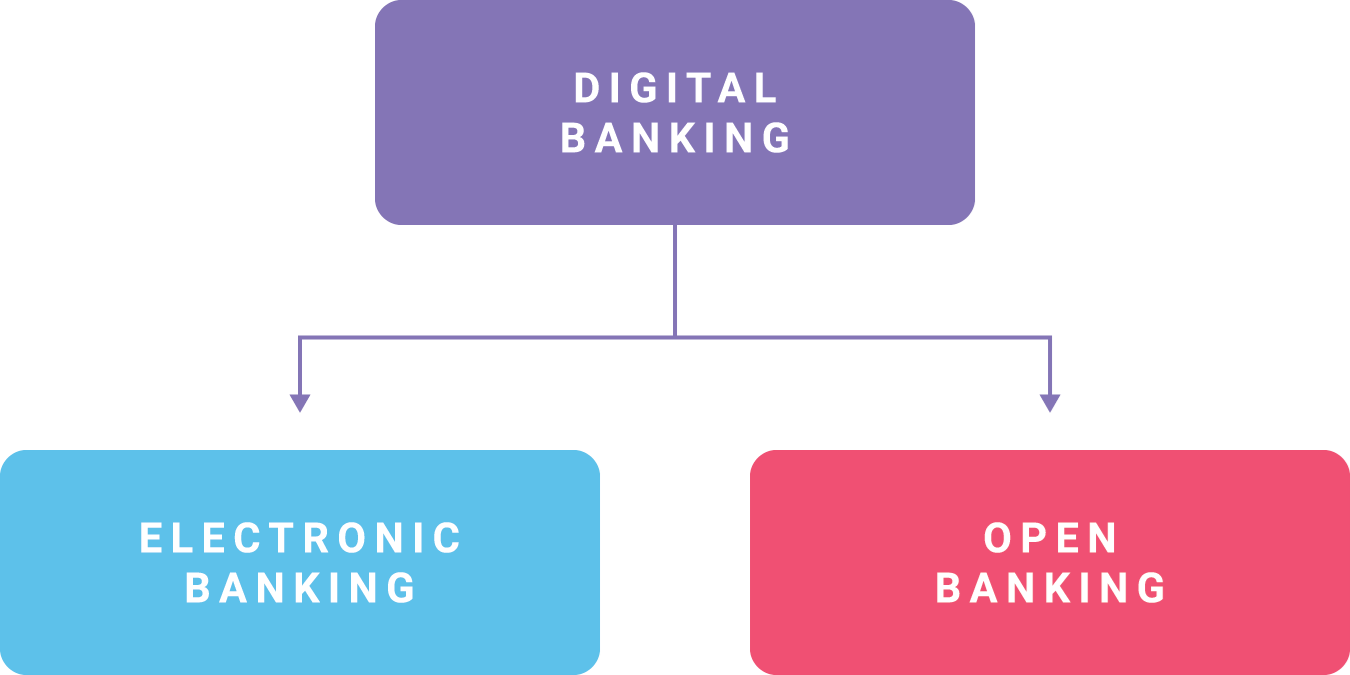
If you work in a financial institution, you may be familiar with using the terms "electronic banking," "internet banking," and "mobile banking" interchangeably. With the publication of the FFIEC's new Authentication and Access to Financial Institution Services and Systems guidance, a new term appeared: "digital banking." The introduction of this new term made me wonder, what does it all mean? Should these terms be used interchangeably and if not, what exactly are the differences among them?
If you are asking the same questions, you've come to the right place. Here is a brief overview of each of these terms, showing how they relate to each other, along with examples of each.
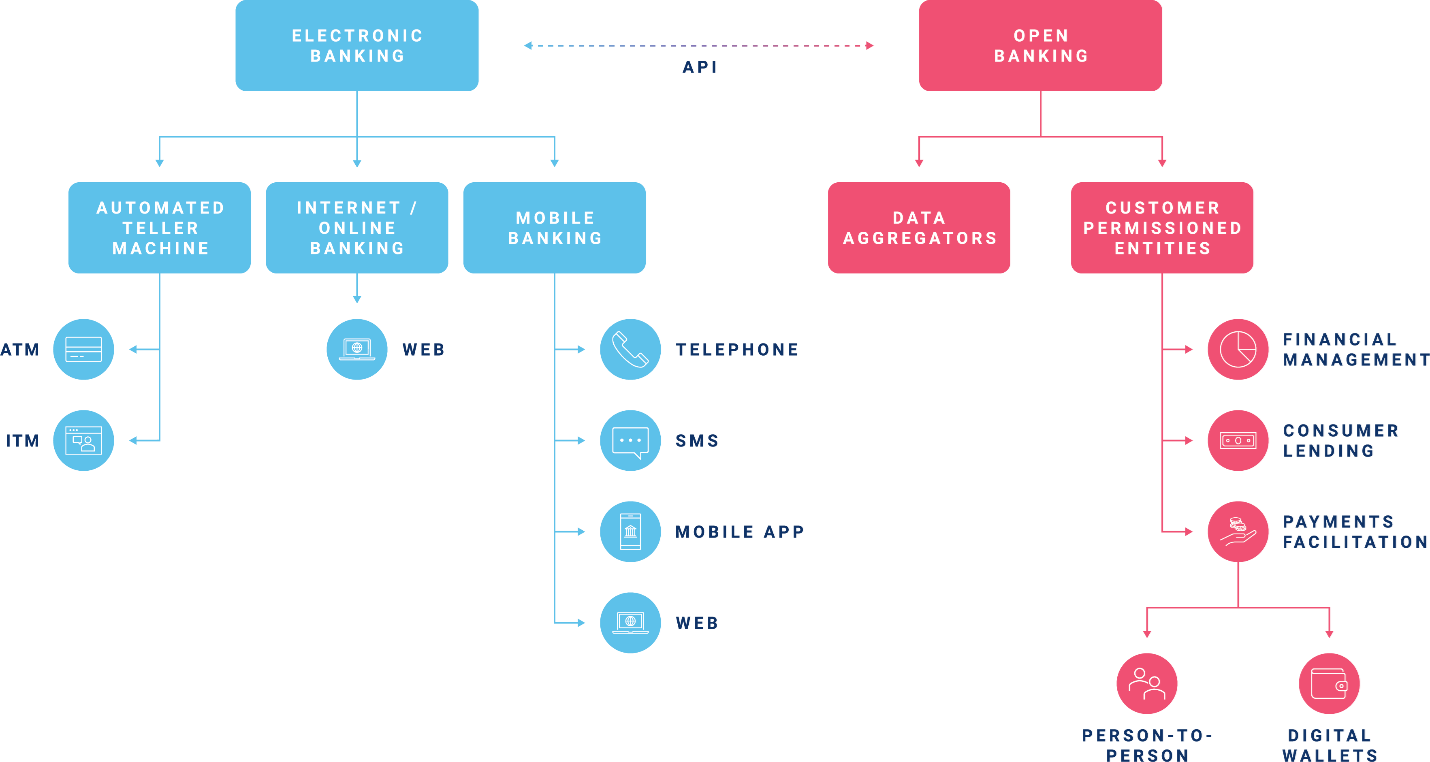
Electronic Banking
A top-level category is "electronic banking" or "e-banking." According to the FFIEC's glossary, e-banking is "the remote delivery of new and traditional banking products and services through electronic delivery channels." This definition is often separated into three pillars.
- Automated Teller Machine (ATM). An ATM is a kiosk which allows a financial institution's customers to perform banking services and transactions electronically without a personal interaction. Common services which can be performed at an ATM include depositing and withdrawing cash, transferring funds, and checking account balances. As ATMs have evolved into Interactive Teller Machines (ITMs), a personal interaction is added back into the equation, while still allowing customers to perform services electronically.
- Internet/Online Banking. The terms "Internet Banking" and "Online Banking" are interchangeable. Internet banking is the ability to perform electronic banking services and transactions via the internet. Common services which can be performed via internet banking include bill pay, funds transfers, viewing statements, contact information updates, etc. Internet banking services can be accessed via web browser.
- Mobile Banking. Mobile banking is the ability to perform electronic banking services and transactions via telephone and/or mobile cellular device (e.g., smartphone, tablet, etc.). Mobile banking services are most often associated with banking via mobile app. But mobile banking also encompasses banking via phone call, SMS / text message, and mobile-enabled web browser. In addition to internet banking services, mobile banking also offers features like mobile deposit capture and integration with "open banking" services.
Open Banking
While the term "open banking" does not appear in FFIEC guidance, this appears to be the current industry-accepted term for the use of third-party service providers who perform electronic banking services and/or transactions through use of an application programming interface (API).
While "open banking" is an evolving topic, the FFIEC's new authentication guidance primarily focuses on what they refer to as "data aggregators and customer-permissioned entities" (CPEs). These entities are third parties who can "access [a] financial institution's customer account information directly" and then use this information to provide services to customers. Some examples of this include:
- Data aggregation services (e.g., Finicity, Plaid, MX, Yodlee, etc.)
- Personal financial management services (e.g., Credit Karma, Mint, QuickBooks, etc.)
- Consumer lending services (e.g., Affirm, Earnest, SoFi, etc.)
- Payments facilitation services
- Digital wallets and assets (e.g., ApplePay, Google Wallet, Paxos, Coinbase, Robinhood, etc.)
- Person-to-person (e.g., Paypal, Venmo, CashApp, Zelle, etc.)
For all intents and purposes, in the same way that "mobile banking" iterated on "internet banking," "open banking" is now iterating on "mobile banking." It is taking traditional electronic banking services and making information and funds more accessible to customers.
Okay, so… Where is Digital Banking?
Right now, there are three primary perspectives on where the term "digital banking" fits into the picture. To explain why, we need to start with the FFIEC's definition from their new authentication guidance.
"Digital banking refers to any banking service or platform that utilizes internet or mobile cellular network communications for providing customers with banking services or transactions."
With this definition in mind, let's talk about the three camps. We'll call them "Camp Synonym," "Camp Subcategory," and "Camp Umbrella."
Camp Synonym
The first camp uses the terms "digital banking" and "electronic banking" interchangeably. This is understandable because the definition harmonizes with the FFIEC's definition of e-banking. It is also probably a more historically accurate and commonly used version of the term. However, this camp begs the question: If "digital banking" is the same as "electronic banking," why did the agencies choose to use a new term and definition? The world may never know.
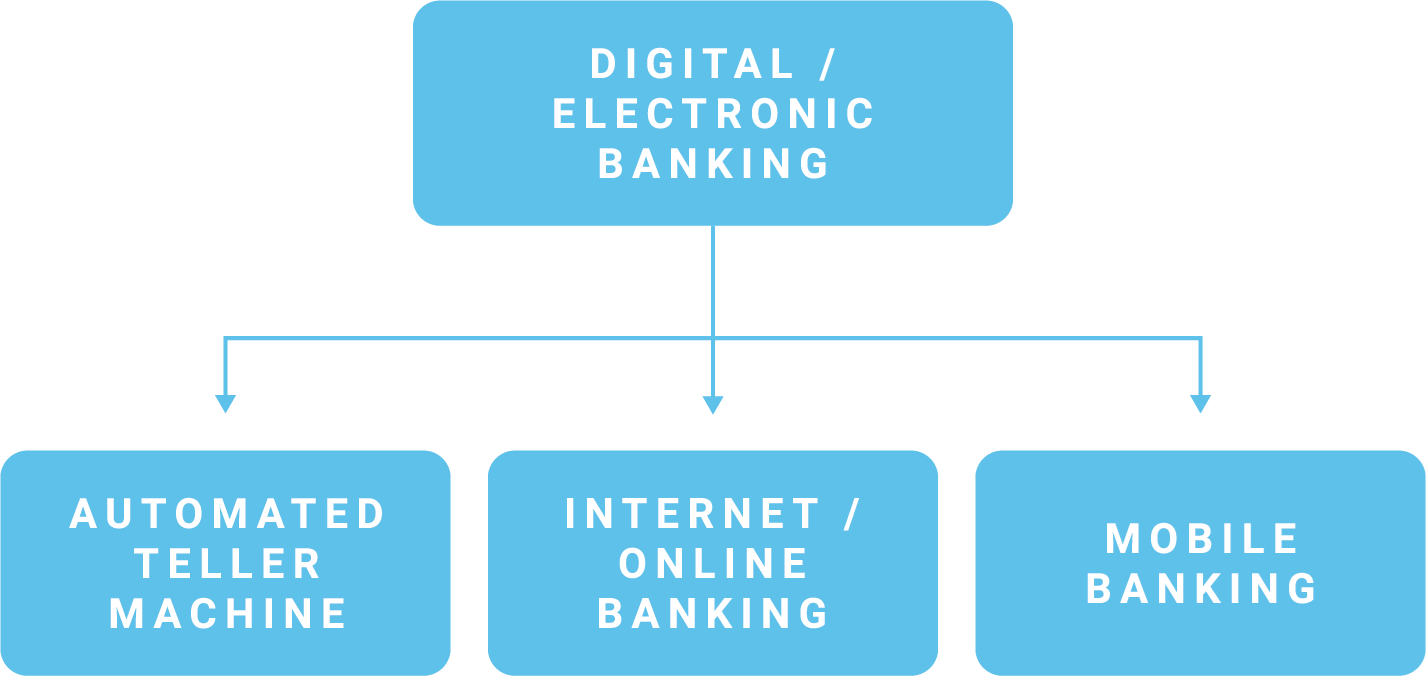
Camp Subcategory
The second camp is a more literal interpretation and would place "digital banking" as a subcategory of "electronic banking." The reason for this is because the definition only mentions "internet or mobile" communications, and intentionally excludes ATMs. This is a notable change from the FFIEC's former E-Banking Booklet and the 2005 authentication guidance (Authentication in an Internet Banking Environment), both of which mention ATMs in relation to electronic banking.
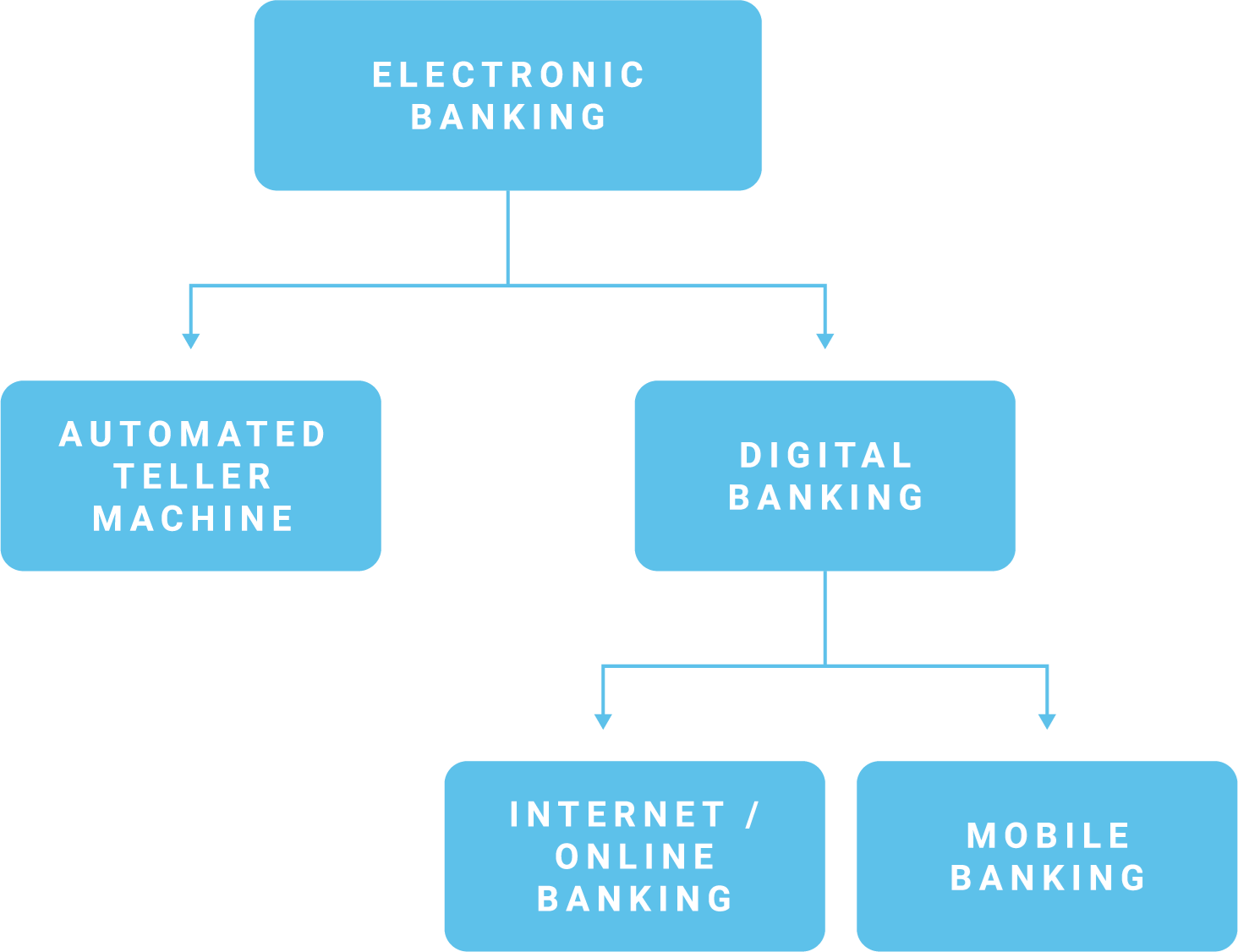
Camp Umbrella
The third camp is a big picture camp and would place "digital banking" as the umbrella term for the relationship between "electronic banking" and "open banking." This perspective stems from the definition's use of the phrase "any banking service or platform." This definition goes hand-in-hand with the new authentication guidance's heavy focus on not only the financial institution's electronic banking systems, but also those accessed, used, or originated by a third-party service provider.
In Short…
I don't like camping. My ideal version of camping is renting a hotel room in a place surrounded by trees with running water, electricity, and regular pest control. That said, if you're a camper, feel free to pick a camp and have a great time.
The term "digital banking" is relatively new to industry guidance. It is currently unclear what this term is, how it fits into the bigger picture, and if it is going to stick around or if people will continue to use the more familiar terms.
Additional Internet Banking Resources
Check out Tandem Internet Banking Security. This online web application is designed based on FFIEC guidance to help financial institutions assess the authentication, third party, and other cybersecurity risks associated with internet banking services. It integrates with Tandem Risk Assessment to provide a comprehensive approach to information security risk management. To learn more, visit our website: Tandem.App/Internet-Banking-Risk-Assessment-and-Security-Software.