In our recent State of Cybersecurity survey, we set out to find any trends among U.S. financial institutions when it comes to budgeting for IT and cybersecurity. Insight from 237 responding cybersecurity professionals helped us see how financial resources are being used to increase the security posture of responding financial institutions.
Remaining Steady
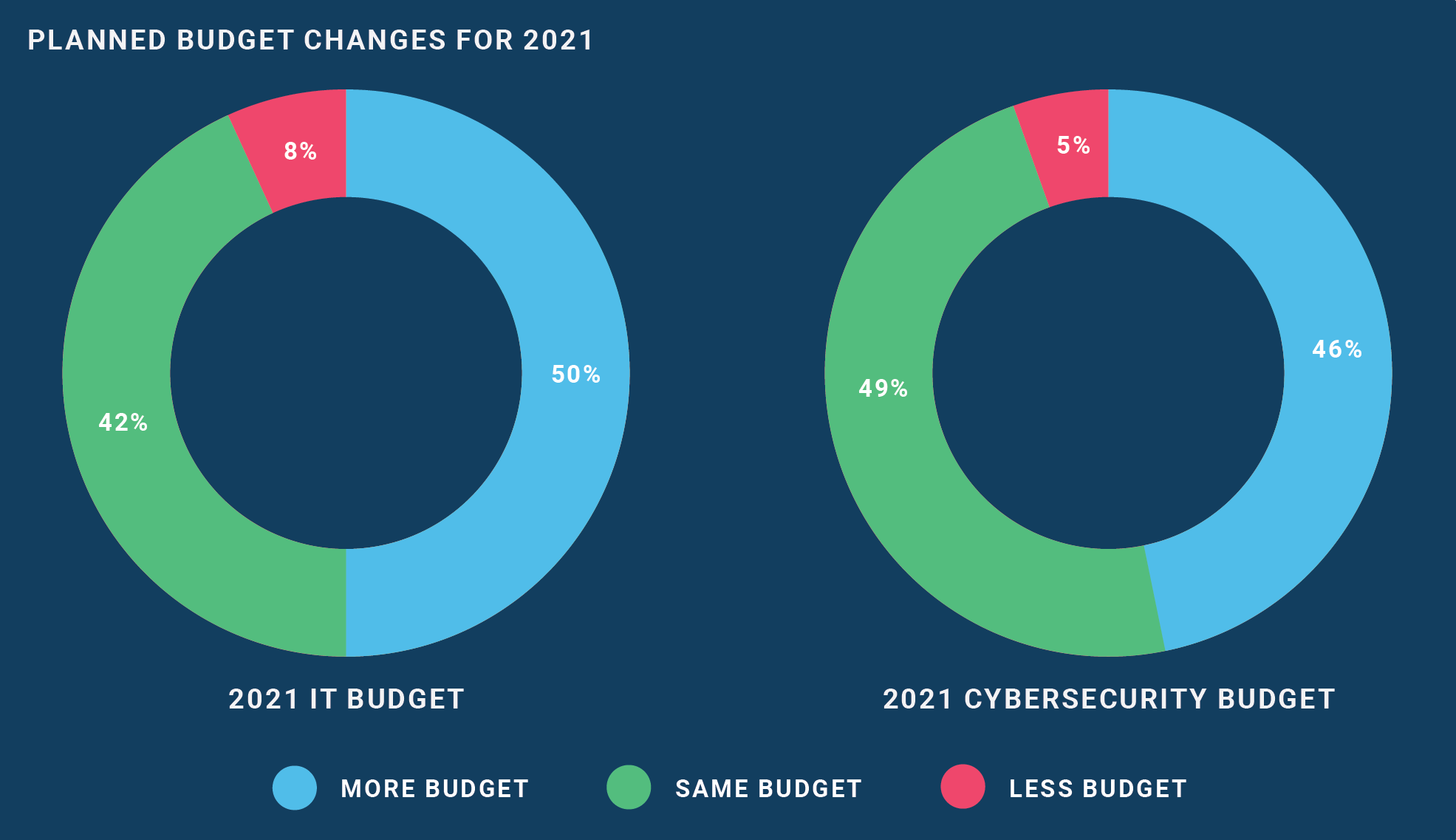
For 2021, we discovered 92% of surveyed financial institutions plan to keep their IT budget the same or increase it in the coming year. Technology is always evolving and cyber threats are ever-changing, so it seems natural to see attention in the budget given to information technology (IT) and cybersecurity. Our metrics from 2020 and 2019 show these budget plans are typical. However, significantly fewer financial institutions plan to decrease their budgets in 2021 (8%), as compared to 2020 (28%). Despite changes due to COVID-19, most budgets are in-line with previous years.
Allocating for Cybersecurity
It is helpful to distinguish between IT and cybersecurity for the purposes of management and compliance. IT encompasses the implementation and management of systems which house an organization's data. Cybersecurity is concerned with protecting the systems and data from threats via the internet.
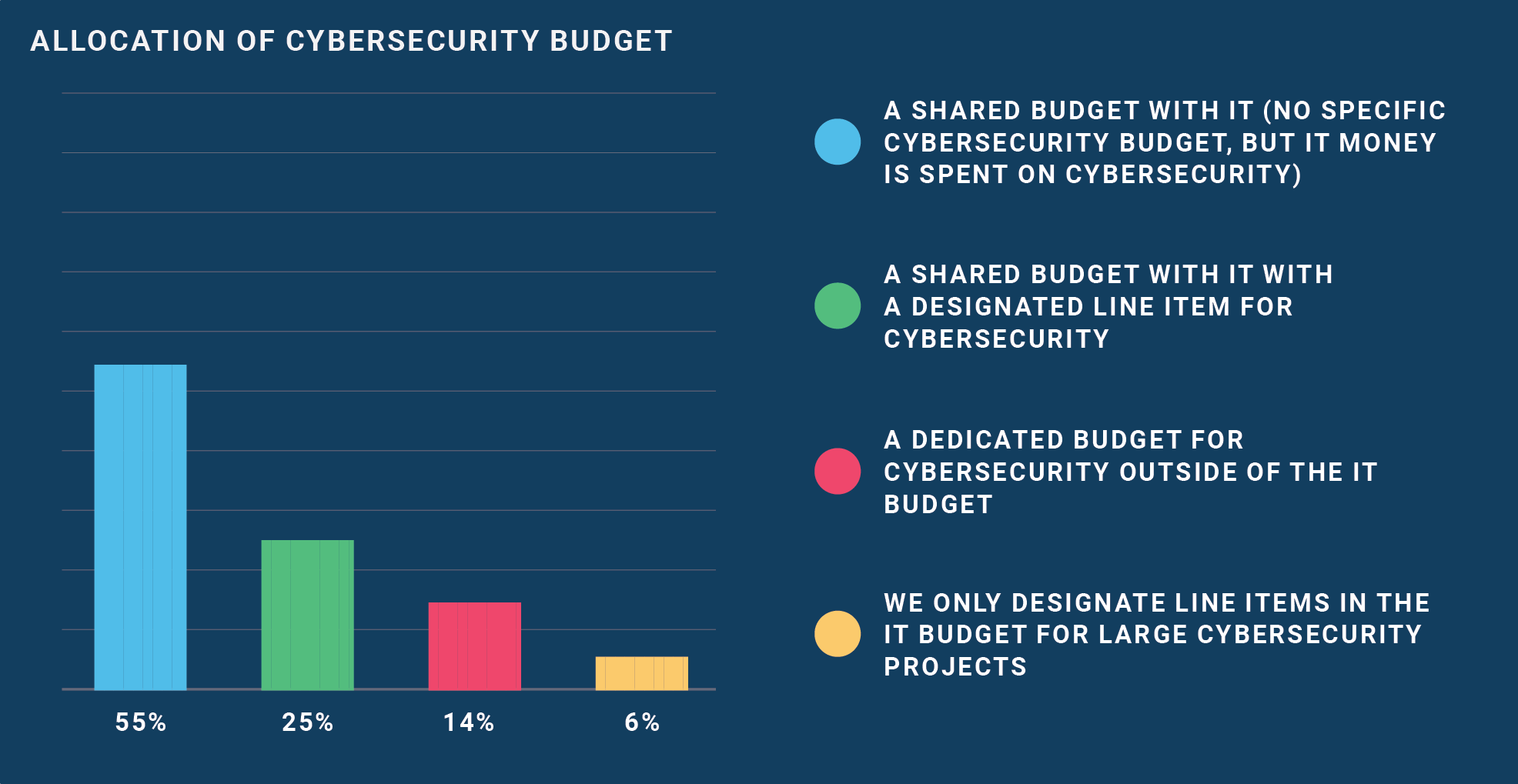
Although IT and cybersecurity are closely related, it is important to distinguish them as separate components within an organization. However, results from our survey found only 14% of institutions have a dedicated budget for cybersecurity outside of the IT budget. A majority of institutions who spend money on cybersecurity, either lump it into the IT budget or include it as a line item of the IT budget. For institutions wanting to be more cyber resilient, it's important to consider having a separate budget dedicated to cybersecurity to ensure security is accounted for in future technology projects.
Moving to the Cloud
At the beginning of 2020, many businesses responded to the COVID-19 pandemic by making changes to their IT environment. Employees were given the ability to work remotely. Collaboration technology was employed to help with social distancing. The increased adoption of mobile technology brought about changes in cybersecurity risk.
Among survey responders, 34% say COVID-19 caused their institution to increase cybersecurity funding for 2021. We also saw a 6% increase in institutions planning to increase their budget for cloud services. The analysis suggests the increase could indicate institutions are moving towards cloud-based solutions to better support remote work environments.
Besides increasing funds for cloud services, institutions also plan to spend more on mobile banking, fraud protection, network infrastructure, and other technology. Several institutions also anticipate spending more on security testing, IT compliance, and enterprise risk management.
Considering Options
The sudden shift to remote environments due to COVID-19 presented new challenges for both IT and information security. Some institutions increased budgets to cover the costs of implementing and securing new remote work technologies. Other institutions find themselves trying to mitigate increased risk while working within the same budget.
While attempting to reduce cost and still ensure an effective security posture, some institutions are likely to increase outsourcing. Outsourcing should be approached with due care, as it can introduce a different set of risks. If outsourcing is on your radar, a conversation with one of our trusted Tandem Partners could provide some direction.
For more interesting trends in how financial institutions are handling cybersecurity, check out our full report at: https://tandem.app/state-of-cybersecurity-report.


